1. Define electricity
2. Draw and label an atom
3. State what causes electricity
4. Draw an electric circuit and show different components in an electric circuit
5. State at least one function each of the components in an electric circuit.
Atom: An atom can be defined as the smallest unit of matter. It contains the neutron, proton and electron. Atoms combine to form molecules. E.g.
Carbon Atom Hydrogen Atom
Structure of an Atom: e.g. Carbon Atom (above)
Neutron: This is the part of an atom that has no charge .It is neutral. It is found in the nucleus of the atom.
Proton: This part of the atom carries the positive (+) charge. It is found in the nucleus.
Electron: The electron is the negatively (-) charged particle of an atom.
It moves freely round the shell.
Matter: Matter is anything that has weight and can occupy space.
Matter is made up of very tiny particles.
State of Matter
Matter exists in three states, namely solid, liquid and gas.
1. Solid: As solid, for instance, ice block. It has a definite shape. The particles move within their fixed position.
2. Liquid: As liquid, e.g. water, matter takes the shape of the container. As such, the particles collide with one another and with the wall of the container.
3. Gas: As gas, i.e. steam in this case, the particles collide faster with one another, with the wall of the container and finally escape into atmosphere.
Electricity
Electricity can be defined as the flow of free electrons in a material. Such materials are called conductors. These free electrons produce electric charges which results in electricity.
Types of Electricity
(i). Static Electricity: This is the flow of charges experienced when two different materials are rubbed together. The flow of charges here is usually very brief. E. g , rubbing one’s palms together or rubbing a biro case on one’s hair.
(ii). Current Electricity: This refers to the steady flow of electric charge from a generating source. The flow experienced here is steady for a long time. E. g . batteries, A.C. and D.C. generators.
Conductors: These are materials that electric charges can flow through. They include materials like water, metals, zinc, copper, etc.
Semi- conductors: These are materials that behave as conductors and insulators. They have both properties. Silicon is an example.
Insulators: Insulators are materials that electric charges cannot pass through. They include materials like dry stick, rubber, plastic, etc.
Charges: A body is said to be charged when it acquires electrons from another object when the two are rubbed against each other. Positive charge naturally flows in the direction of the negative charge. E.g.
Positive charge flowing towards Negative charge
Polarity of Charges.
This is a condition where electric charges are at opposite terminals. These charges could be referred to as like and unlike charges. In electricity, these charges are referred to as positive (+) and negative (-) charges.
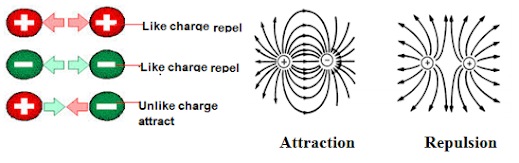
Law of Electric Charges
This law states that like charge repel while unlike charge attract. E.g.
Attraction Repulsion
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1.Define matter
2. Define an atom
3. Identify the three state of matter
4. Differentiate between conductor and an insulator
5. Define electric charge and draw the hydrogen atom
6. Explain


Comments
Post a Comment